What Is A Drone? How Does It Fly? Types, Pros & Cons | 2025
Drones, also known as Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs), have become increasingly popular in recent years. They are used for a wide range of applications in different industries and can offer many benefits over traditional methods.
In this article, we will discuss what a drone is and the different types of drones available. We will also explain how drones work, and their potential uses in various industries.
We’ll also discuss legal considerations when using drones and safety and privacy concerns that need to be considered.
Lastly, we’ll look at the advantages and disadvantages associated with drone technology. By the end of this article, you should understand what drones are and how they can be used in various industries.
Table of Contents
Definition of a Drone
A drone is an unmanned, autonomous aerial vehicle (UAV) controlled by either a remote or onboard computer system.
Drones are typically powered by electric motors and equipped with navigational systems such as GPS receivers, gyroscopes, accelerometers, magnetometers, altimeters, and other sensors to help them remain stable while in flight.
They can be piloted manually or programmed to fly autonomously using computer vision and artificial intelligence (AI).
Read Also, Complete Evolution & History of Drones
Components Of Drone
Several components power the propulsion of a drone. These components act together to create lift and thrust that powers the drone.
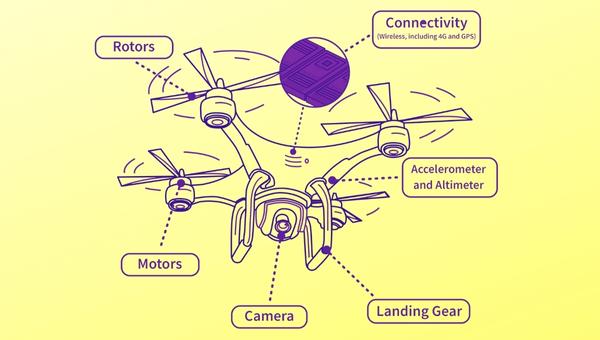
- Motor
- Propellers
- Flight controller
- Speed controllers
- Battery
- ESC (Electronic Speed Controllers)
- Power distribution board
Motor: A motor is the main driver of a drone’s propulsion system, as it supplies the power needed to turn the propellers. The motor needs to be powerful enough to provide sufficient thrust for lift-off and maneuvering in flight.
Propellers: Propellers are responsible for creating lift and thrust from the spinning motion generated by the motor. The blades on the propellers are designed to be angled and spaced to produce a specific amount of thrust.
Flight controller: This component is responsible for controlling the drone’s navigation systems, such as its attitude, altitude, orientation, and speed. It also helps manage tasks like maintaining balance during flight and correcting any inconsistencies in motion control.
Speed controllers: Speed controllers are responsible for managing the speed of the motors and propellers. They are usually integrated into the flight controller and connected directly to the motor.
Battery: The battery provides power to all components on board, including the motor, ESCs, flight controller, and other electronics like lights. The battery must be able to provide enough power to sustain the required lift and thrust for a safe flight.
ESC (Electronic Speed Controllers): ESCs are responsible for regulating and controlling the speed of brushless motors. They convert the electrical signals from the flight controller into mechanical rotations for each motor, as well as regulate power output and keep the motor from overheating.
Power distribution board: This is a circuit board that distributes power from the battery to each of the motors and ESCs on the drone. It helps minimize voltage loss and ensures each component receives the correct amount of power needed for optimal performance.
By combining all these components, drones are able to fly safely, efficiently, and with agility. With advancements in technology like more efficient motors and batteries, drones are continuing to become lighter and more powerful.
How do Drones work?
Drones use a combination of sensors, remote control, and autonomous navigation to maneuver through the air.
The most common type of drone is an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV), which is an aircraft that is flown without any direct human involvement.
UAVs can be remotely controlled or fly autonomously based on preset programming.
To control a drone remotely, the user interacts with a controller that sends commands to the aircraft. These commands can be used to direct the drone’s motion or program into it an autonomous flight path.
The Mechanism Behind It
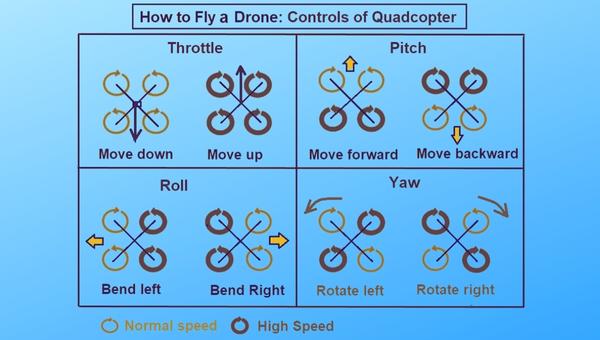
A drone is typically powered by four rotors, each with an electric motor attached to a propeller. The motors spin the propellers to produce thrust, which pushes the drone up into the air and allows it to fly.
As these motors are controlled independently, they can be used to provide thrust in any direction, allowing the drone to move forwards, backward, up, and down.
When the drone is operating in autonomous mode or controlled remotely, a range of sensors is used to help it navigate its way around.
These include an Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU), which measures acceleration and angular velocity; Global Positioning System (GPS) receivers that provide positioning data; magnetometers which measure the relative strength of magnetic fields; and sonar sensors which help detect objects in close proximity.
Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU)
An Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) is a type of sensor used in drones to measure and report on changes in angular velocity, acceleration, and orientation with respect to the drone’s frame of reference. It consists of three components: an accelerometer, a gyroscope, and a magnetometer.
The IMU is often integrated into the drone’s flight controller, which uses this data to calculate the drone’s position, orientation, and height in order to keep it stable in flight.
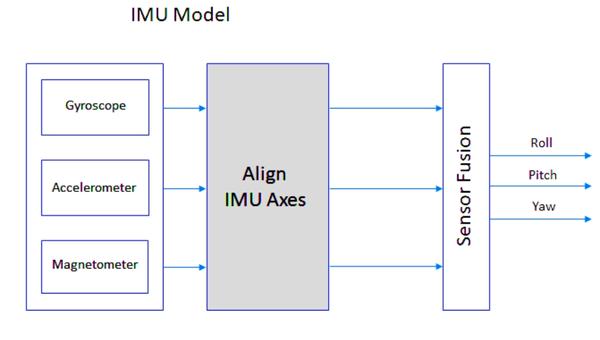
Additionally, the IMU can be used for other advanced operations, such as obstacle avoidance or automated navigation.
In some cases, a GPS receiver is used in combination with the IMU for increased accuracy. This allows drones to have autonomous capabilities and operate without continuous human guidance or control.
Gyroscope
A gyroscope is a type of sensor used in conjunction with the IMU to measure and report on changes in angular velocity. It consists of one or more spinning discs that rotate around an axis at different rates, depending on the direction and speed of motion.
This data is then used to maintain stability during flight since it can detect even the slightest changes in direction.
How does Gyroscope work?
The Gyroscope system works by sensing and measuring the angular velocity of the drone. The angular velocity is measured in three dimensions – pitch (rotation around the x-axis), roll (rotation around the y-axis), and yaw (rotation around the z-axis). These rotations are then combined to form a vector that can be used to inform the drone’s flight path.
The data provided by the gyroscope is fed into the flight controller, which uses it to adjust and maintain the drone’s orientation in space.
This allows for increased stability during flight, as well as more precise control over its movements.
It also helps reduce the risk of crashing since the drone can detect even the slightest changes in direction and respond appropriately.
Accelerometers
Accelerometers are usually made of piezoelectric materials, such as quartz crystals. When an external force is applied to the accelerometer, it will deflect in one direction, resulting in a voltage or current output proportional to the acceleration experienced.
This output can then be used by the drone’s control system to measure acceleration and adjust the drone’s flight path accordingly.
For example, the accelerometer can be used to detect when a drone is climbing or descending, and the control system can adjust the throttle accordingly to keep it at a constant altitude.
How do Accelerometers work in drones?
Accelerometers in drones measure changes in acceleration and then send this information to the drone’s flight controller, which uses it to adjust the propellers’ speed, ensuring that the drone maintains stability while in flight.
The accelerometer also provides feedback on movements made by the user (such as tilting or propelling), allowing users to control their drone’s movement more accurately and efficiently. Additionally, they provide data on changes in altitude so that the drone can maintain a predetermined altitude when flying.
Magnetometers
A drone’s magnetometer works in a similar fashion to that of an airplane. It is a device used to measure the direction and strength of magnetic fields. This helps the drone determine its orientation and maintain proper heading while maneuvering in the air.
Magnetometers are also useful for maintaining altitude during flight, as they can detect changes in the earth’s magnetic field in order to adjust altitude accurately. This is especially useful for drones used in surveying and mapping applications.
The magnetometer on a drone is typically located near the main flight controller and other sensors, so it can collect data quickly and accurately as the drone moves through different areas.
Distance Sensor
A distance sensor is a type of sensor used to detect the distance between two objects. It can be used to measure the distance between a drone and an object, allowing the drone to navigate around obstacles and stay at a safe operating distance.
The precision and accuracy of distance sensors vary depending on their type and design, but they are generally reliable for basic navigation tasks.
How do Distance sensors work in drones?
Distance Sensor uses a combination of various sensors in order to detect obstacles and measure distances. This includes infrared sensors, ultrasonic transducers, stereoscopic cameras, and laser rangefinders.
This sensor also allows the drone to accurately measure distances between objects, helping it maintain its course.
Types of Drones
Drones come in all shapes and sizes, from large military drones used for surveillance to small consumer drones used for photography.
The most popular types of drones are those that are designed for recreational use, such as racing or photography. These drones typically have four rotors, and a camera mounted on the front. They are relatively easy to fly and can be used to take pictures or videos.
Other types of drones include multi-rotor drones, which have six or more rotors, as well as hexacopters and octocopters. These are larger and more complex drones that are often used for aerial photography, search and rescue operations, or military surveillance.
Finally, there are also commercial drones, which can be used for a variety of purposes, such as package delivery. They are often larger and more expensive than consumer drones, and the FAA heavily regulates their use in the United States.
Uses and Applications of Drones in Different Industries
Drones are being used in a wide range of industries, from agriculture and construction to media and entertainment.
In the agricultural industry, drones are being used to monitor crops and track soil moisture levels. This helps farmers identify areas that need more fertilizing or water to improve efficiency and yield. Meanwhile, in the construction industry, drones are being used to map and inspect buildings, bridges, and roads.
The media and entertainment industry also leverages drones for aerial photography and cinematography. The increased stability of drones makes them ideal for capturing footage from angles that were once difficult or impossible to achieve with traditional cameras.
In addition, drones are being used by the military and law enforcement to provide situational awareness in dangerous or hard-to-reach areas.
The possibilities of drone technology are endless, with new applications emerging every day. As this technology progresses and more industries adopt it, we can expect to see even more creative uses for drones in the future.
Read Also, New Drone Laws In The USA | All You Need To Know
The legality, safety, and privacy considerations when using Drones
Drones have become increasingly accessible, which means the responsibility to use them safely and legally falls on the owner. Laws vary from country to country and even state to state in some cases.

Depending on where you are flying your drone, it may be prohibited or require a special permit or license. In addition, drones must adhere to height restrictions ( usually not higher than 400 feet) and stay clear of airports and air traffic.
In the United States, the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) is the main agency responsible for air safety and drone regulation. The FAA has several regulations that apply to drones, including registration requirements, altitude restrictions, and no-fly zones.
It is important for drone owners to familiarize themselves with the safety and legal considerations of using drones, as failure to do so may result in fines or criminal charges.
General Drone Rules
When flying a drone, it is important to remember the following rules:
- Fly responsibly and always follow local laws
- Keep your drone within sight at all times
- Do not fly over people or animals
- Do not fly near airports, military bases, or other sensitive locations
- Do not fly in bad weather conditions
- Do not fly above 400 feet
- Make sure to register your drone with the aviation authority in your country.
Adhering to these rules is essential for safe, responsible flying and will help ensure that drones remain a viable tool for years to come.
Privacy is also an important consideration when using drones. Depending on where and how it is used, a drone can potentially invade someone’s privacy or interfere with their normal activities. It is always best to seek out permission before flying a drone in populated areas, such as public parks, cities, and other areas where people may be present.
Read Also, 30 Major Pros and Cons of Drones
Advantages of Drones
Drones are used for a variety of purposes, and they come with many advantages.
1. Enhanced Surveillance: Drones can be used to observe and monitor land, sea, or sky areas that are difficult or impossible for humans to access. This makes them ideal for surveillance applications such as border patrol, pipeline inspection, and environmental monitoring.
2. Improved Delivery Services: Drones can be used to deliver packages quickly and efficiently to hard-to-reach areas. This allows companies to reduce delivery costs and improve customer satisfaction.
3. Precision Agriculture: Drones can be used for precision agriculture, which involves using aerial imagery to monitor crop health, detect weeds, measure soil moisture content, and track pest infestations. This helps farmers increase crop yields and optimize the use of resources.
4. Search and Rescue: Drones can help search for lost people in remote or dangerous areas, helping speed up rescue operations. They can also be used to deliver supplies such as food, water, and medical equipment to those stranded and unable to access traditional help.
5. Recreational Fun: Drones are becoming increasingly popular as toys and recreational vehicles. They can be used to capture aerial footage of scenery, engage in drone racing, or take part in other activities that would otherwise not be possible.
6. Military Applications: Drones are becoming an essential tool for military operations because they provide real-time intelligence and reconnaissance. They are being used for surveillance missions, target acquisition, and even deployment of munitions.
7. Emergency Services: Drones can be used by emergency services personnel to survey the scene of an accident or incident quickly and gain insight into the situation before they arrive on the scene. This helps to reduce the response time and improve safety.
8. Scientific Research: Because drones can access remote or hard-to-reach areas, they are being used by researchers to collect data on the environment, examine geological features, and take measurements of landforms. This helps to improve our understanding of the world around us.
9. Weather Monitoring: Drones are being used to gather data on weather patterns and monitor the atmosphere over large areas. This helps meteorologists predict severe weather conditions, track storms, and provide more accurate forecasts.
10. Disaster Relief: Drones can be used to assess damage and destruction caused by natural disasters such as floods, hurricanes, and earthquakes. This helps to improve the speed of disaster response and increase the effectiveness of relief efforts.
Disadvantages of Drones
Despite their numerous advantages, drones also come with some drawbacks.
1. Safety Risks: Drones can pose a safety risk to people and property if they are not operated correctly. They are particularly dangerous when flown in close proximity to airports or other controlled airspaces.
2. Legal Issues: The legal implications of using drones for commercial or recreational purposes are still being debated. Many countries have laws restricting drone use and airspace, so it is important to familiarize yourself with local regulations before flying a drone.
3. Cost: Drones can be expensive, especially for more advanced models that come with cameras and other features. This may make them prohibitively expensive for some people.
4. Maintenance: Drones require regular maintenance and servicing to ensure that they are operating correctly and safely. This can be costly, time-consuming, and complicated for inexperienced users.
5. Limited Battery Life: Most drones have a limited battery life, which means that their flight times are usually quite short. This makes them unsuitable for extended operations or missions.
6. Data Security: Drones can collect sensitive data that must be kept secure and protected against potential threats. Without proper security measures in place, this data could fall into the wrong hands and be misused.
7. Privacy Concerns: The use of drones has raised privacy concerns, as they are typically equipped with cameras and other sensors that can collect data on individuals or properties. Some countries have laws in place to protect citizens’ privacy, but there is still a need for stricter regulations in this area.
8. Interference: Drones can be affected by wireless interference from other devices, which may cause them to crash or lose connection with their controllers. This is especially true in areas with high levels of electromagnetic activity.
Conclusion
Drones have a wide range of applications, from military operations to scientific research and disaster relief. They can be invaluable for gathering data in hard-to-reach areas or dangerous environments.
However, some drawbacks are associated with drones, such as safety risks, legal issues, cost, maintenance requirements, and limited battery life. Additionally, privacy concerns and interference from other devices remain potential problems that must be addressed when using drones.
With careful consideration of the advantages and disadvantages of this technology, it is possible to make informed decisions about how best to use them safely and legally for various purposes.
We hope this article has improved your understanding of drones and their capabilities. Thank you for reading!